For over a decade Google Analytics offered web analytic service which tracks and reports website traffic. Then in 2012 Google announced a release of a new tool – Google Tag Manager. It’s a common misinterpretation that Google Tag Manager is completely the same thing as Google Analytics, but it’s not. Another thing is that there is still a lot of confusion about GTM, what it is exactly, how does it work, is it complicated for using etc. That’s why we decided to introduce you to it in the simplest possible way, and help you understand how powerful and useful this tool can be for you.
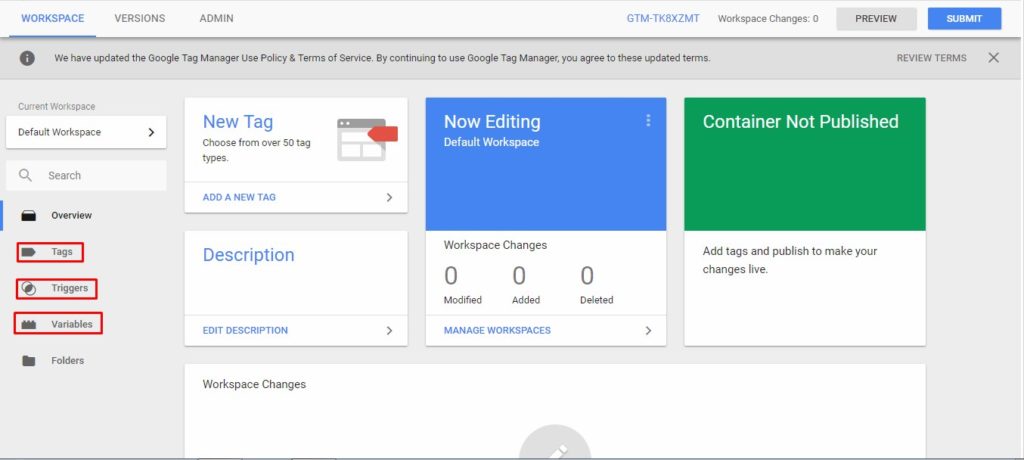
Google Tag Manager consists of three parts:
Tag – a snippet of code added to a page.
Triggers – which define where and when should the tags be executed.
Variables – which receive and store information that is useful and which tags and triggers can use.
Simply, Google Tag Manager is a tool that manages tags, or snippets of code (mostly JavaScript) which send information to third-parties. It simplifies a process of adding these snippets, because you use the interface to decide what and on which page you want, instead of updating the whole additional code on your website. After that Google Tag Manager adds needed tracking to your website, in order to make sure that everything is running smoothly.
Before Google Tag Manager was released JavaScript on your app or website had to be hard-coded, which was complicated because you couldn’t do that by yourself, and it would often take too long. Now, everything is so much easier. Google Tag Manager really does have a user-friendly interface and introduces you step-by-step so that you can create a tag, which in the end means that you don’t have to have advanced skills when it comes to JavaScript.
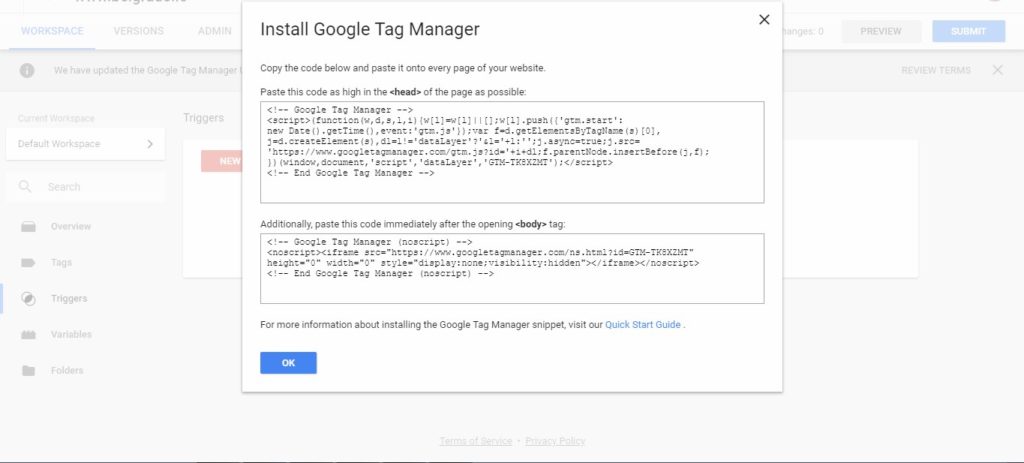
In order to start, just add the container tag – custom generated tracking code to your website. After you are done, Google Tag Manager will allow to anyone with suitable permission to add, debug or change tags. Most importantly you can create tags by yourself, track them and change them however you want, without having a developer by your side.
I have already mentioned that there was a misconception about Google Tag Manager and Google Analytics and that these are separate tools which can work independently. But, you would be surprised how well and in how many ways they can work together.
There few most common ways of using these two tools together. For example, you can use Google Tag Manager to send pieces of data like events or pageviews to Google Analytics. I have to mention that you will have to add JavaScript to your website, but you don’t need it for using Google Tag Manager itself.
Let us finish with just one example of how to send data to Google Analytics by using Google Tag Manager. If you would want to track resource downloads on your site either pictures or documents, you will have two main tasks – what page was the user on when it downloaded the file and how many people downloaded the file itself. With Google Tag Manager you can easily set up click triggers and Google Analytics Tag which will show you where and which files were downloaded, and again, you will do this without adding any new or additional code to your website.
Or you would maybe just like to send a virtual pageview to Google Analytics when a user clicks on a link of the file from where it can be downloaded. And the best thing of all is that you can use Google Tag Manager Triggers to dictate when a specific data should be sent to Google Analytics. As mentioned before variations and possibilities are really endless when it comes to these two tools and what they can achieve when working together.

